Embarking on a website migration? Preserving your site’s SEO rankings is likely a top priority. This comprehensive guide and checklist is designed to walk you through the process, ensuring that your migration is a success without sacrificing your hard-earned search engine rankings.
From planning to monitoring and troubleshooting, this checklist covers everything you need to make your migration smooth and efficient.
Whether you’re a seasoned SEO pro or a beginner, the tips and best practices shared here will help you navigate the complexities of website migration and emerge with your site’s SEO performance intact.
Read on to learn more about optimizing your website migration for SEO success.
What is Website Migration?
Website migration refers to any event whereby a website undergoes substantial changes affecting its setup, design, UX/UI, location, and structure that could potentially impact its visibility in search engines. These changes could range from moving to a new site domain to restructuring its content hierarchy, shift from HTTP to HTTPS for better security, or changing your Content Management System (CMS).
A successful website migration requires cautious planning and execution, ensuring that the SEO value built over the years doesn’t diminish.
Regardless of the magnitude of changes, it’s clear that website migration is a significant event with potentially massive implications for a site’s performance, so it’s definitely not a process to be taken lightly.
The Different Types of Site Migrations
Website migrations can be of many types:
- Platform Migration: This includes moving your website to a new CMS. It offers potential improvements in flexibility, interface, and functionality but can pose risks to your existing data and SEO if not handled correctly.
- Domain Migration: It occurs when moving your site to a new domain name. You must be careful to redirect users and search engines to your new site to avoid losing traffic.
- Protocol Migration: Shifting from HTTP to HTTPS for enhanced security is a common migration, but it can affect SEO if not implemented correctly.
- Structural Migration: Changes in the overall site structure, including URL changes, come under this category. SEO can take a significant hit if the changes affect the way search engines crawl and index your site.
- Content Migration: This involves significant changes to your site’s content, like addition, deletion, or alterations. A focus on preserving and improving SEO-friendly content is a must for a successful migration.
Does Website Migration Affect SEO?
The straight answer is, yes! Website migration may cause your SEO to shake up a bit, leading to volatile search ranks, potential traffic dips, and even reduced visibility. These changes occur because search engines need to re-crawl and re-index your website post-migration.
The situation can worsen if mishaps occur during migration — improperly redirected URLs can leave pages missing from the search engine index, hasty changes to content and metadata can knock down keyword rankings.
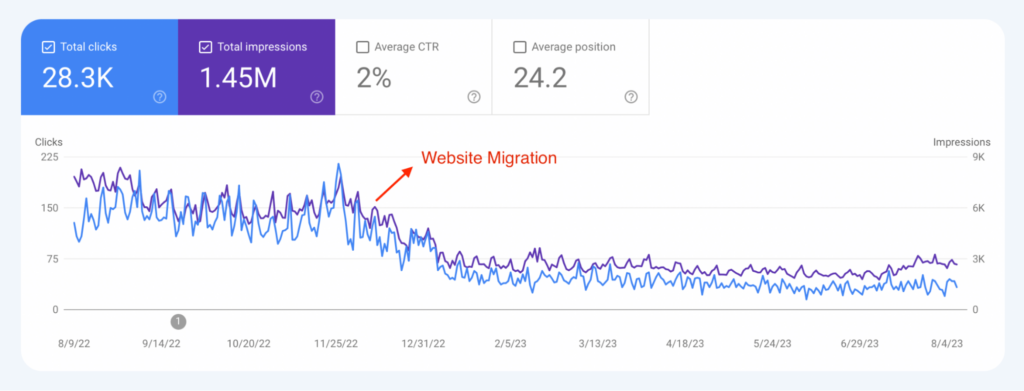
Therefore, it’s not just about migrating the website; it’s about migrating smartly with SEO at the heart of the process.
How Long an SEO Migration Takes?
The duration of an SEO migration depends on several factors including the size and complexity of your website, the type of migration (platform, domain, protocol, structural, or content), and the resources available.
As a general rule of thumb, it might take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months for a complete SEO migration to be executed correctly.
Always remember to factor in enough time for pre-migration audits, the actual migration, testing, and then post-migration analysis for a successful transition.
Pre-Migration Planning
Before diving headfirst into your website migration, it’s crucial to prepare thoroughly to ensure a smooth transition. Here’s our step-by-step guide to pre-migration planning:
1. Set Clear Migration Goals
The first step in a successful website migration is defining clear objectives. Is the goal to enhance the user experience, update branding, improve site structure, or adopt a more SEO-friendly platform? Knowing what you aim to achieve will guide the steps that follow and provide a benchmark against which you can evaluate the migration’s success.
2. Assemble a Migration Team
Lots of expertise goes into a successful website migration. You’ll need a project manager to helm the operation, web developers for the technical heavy lifting, SEO professionals to minimize organic search impact, and content creators to wield the pen or brush as needed. Assemble your team early and keep the lines of communication open at all times.
3. Perform a Comprehensive Site Audit
A thorough site audit will give you a clear understanding of your current website’s status. Analyze your SEO data, content, site structure, and more. You’re looking for any issues that need fixing – either before the migration or as part of it. Understanding the current state of the website will also help evaluate the impact of the migration.
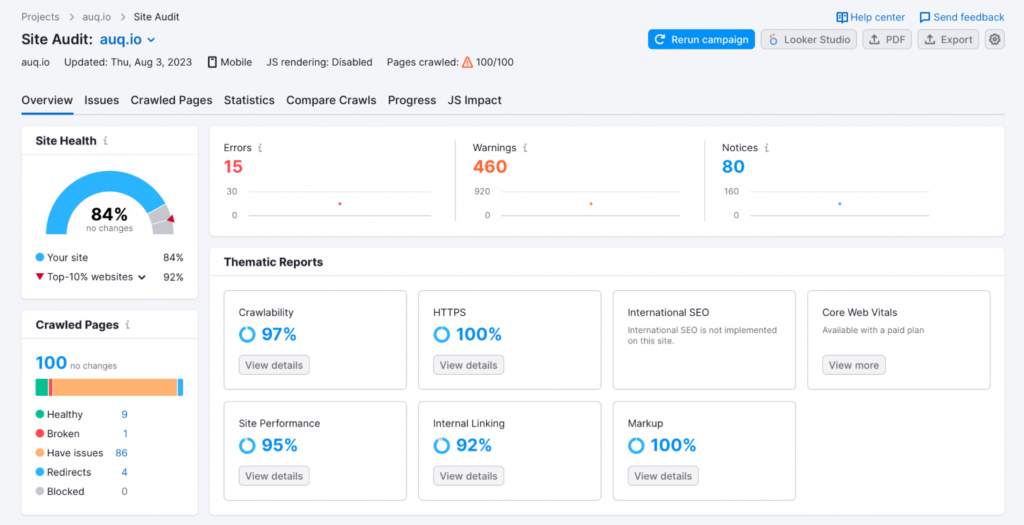
For the SEO audit, you can use a tool like Semrush or Ahrefs.
4. Backup Your Website
Even with the most skilled team and precise planning, things can (and often do) go wrong during website migrations. To safeguard against any unforeseen issues, make sure to back up your website. Protect everything – the content, databases, multimedia files, and more.
This will enable you to restore the site in the event of an emergency. If you don’t have a backup plan in place, your website could be compromised and potentially damaged beyond repair.
5. Setup a Staging Site
A staging site is a clone of your live website. It’s where you make all the changes before going live. Here you can implement, test, and tweak everything without affecting your users or your search engine position.
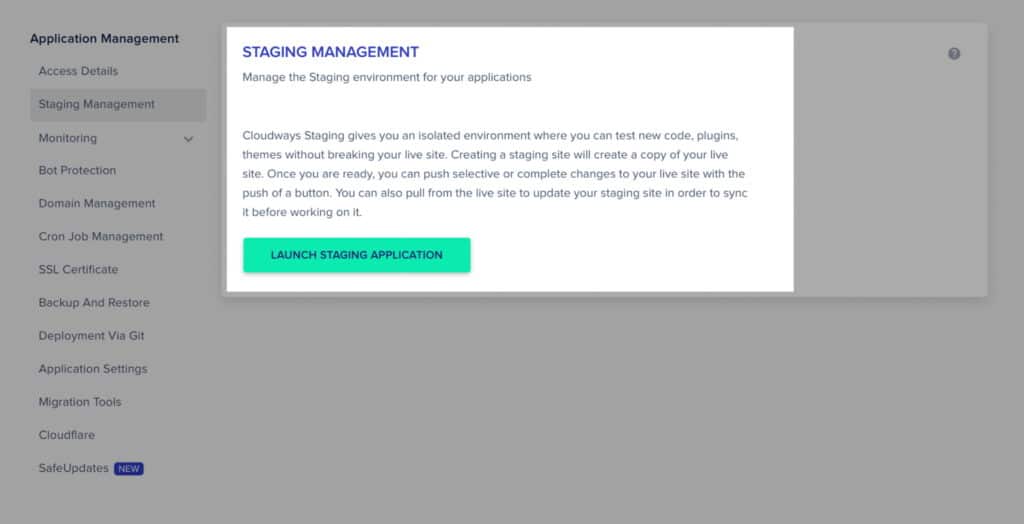
The staging site also makes it easier to roll back changes if something goes wrong. This way, if something goes wrong, the only thing you have to worry about is fixing it. It’s not like you have to start from scratch or lose all your hard work.
6. Plan the Migration Timeline
Figure out the best time to conduct the migration. Remember, you’ll likely see some temporary dips in website traffic and performance post-migration, so consider that in your planning. Also, ensure that all team members are on the same page with the timeline.
The more time you have to plan, the smoother the migration will go. As such, it’s best to start planning your migration at least a month in advance.
7. Inform Your Current Users
Lastly, it’s good manners (and good business) to let your current users know about the upcoming website migration. Whether these are your daily blog readers or paying customers, people appreciate a heads up to potential disturbances in their website visits or service usage.
By telling your users about the migration, you can also help them prepare for any changes. For example, if you’re changing payment gateways or adding new features to your site, let users know what’s coming so they can be ready when the time comes.
Technical SEO Considerations
During your website migration journey, being well-prepared and thorough will ensure the least impact on your search engine rankings and website performance. This guide provides insight into the essential technical SEO considerations to bear in mind throughout the process.
1. Setup Search Console and Webmaster Tools
As a starting point, verify your new website with the Google Search Console and other webmaster tools like Bing or Yandex. This ensures that you have access to your website’s data and can monitor its performance during and after your migration.
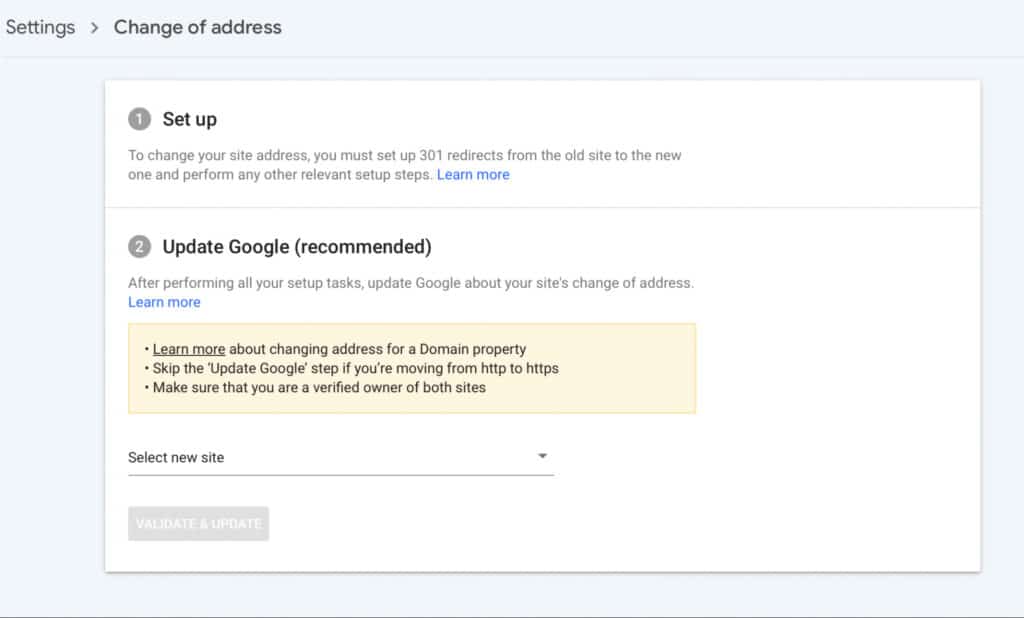
Furthermore, it’s crucial to submit your sitemap and check for any crawl errors.
2. URL Structure and Redirects
One of the primary aspects that can impact SEO during migration is URL structure. Plan your website’s new URLs carefully and map them to the old ones accordingly. Implement 301 redirects for all changed URLs, which reduces the chance of lost traffic and maintains link equity. Use a redirect plan to guide you through this process and regularly test your redirects to ensure their functionality.
3. Ensure Mobile Responsiveness
Google’s mobile-first indexing is no secret — your website’s mobile-friendliness has a major impact on its rankings. Make sure that your new site is mobile-friendly and responsive, and test it thoroughly across various devices before launching.
4. Maintain Site Speed
Fast-loading webpages are crucial for user experience and search engine rankings. Prioritize performance and avoid transferring bloated code when migrating.
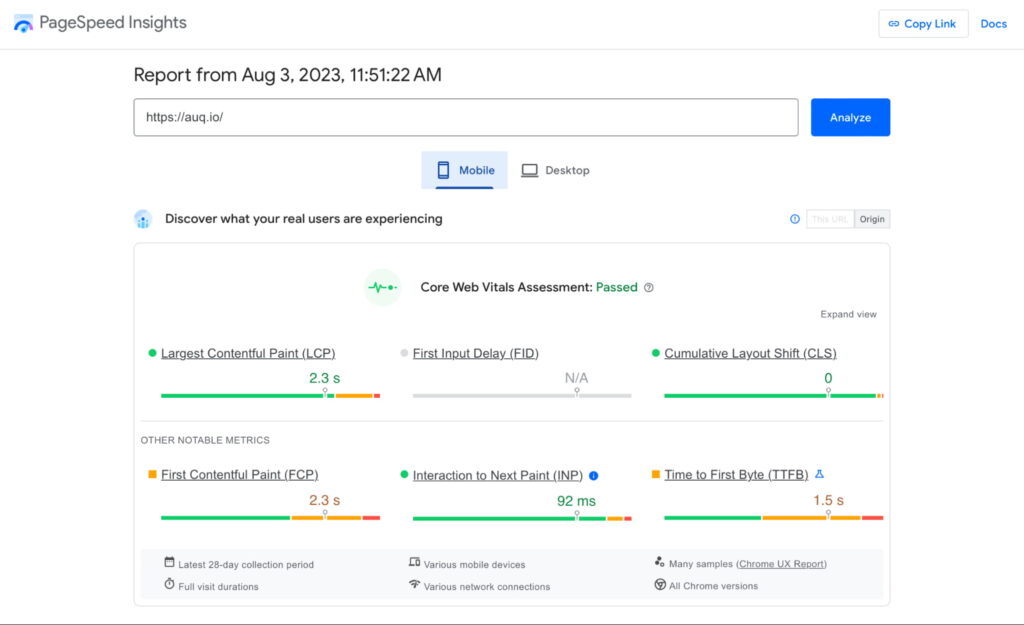
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and WebPageTest to measure and optimize your new site’s loading speed.
5. Secure Website With HTTPS
Security is paramount in today’s digital landscape. If you haven’t already, ensure that your website utilizes HTTPS for a safer browsing experience for your users. Making the switch from HTTP to HTTPS is essential to safeguard both your website and its rankings.
6. Update Your Robots.txt
Don’t forget to update your robots.txt file on the new site, as it controls which pages search engine bots can crawl. Make sure this file allows access to all the necessary pages on your website and, if required, includes the modified sitemap URL.
7. Update Your Backlinks
One of the most valuable SEO assets is a healthy backlink profile.
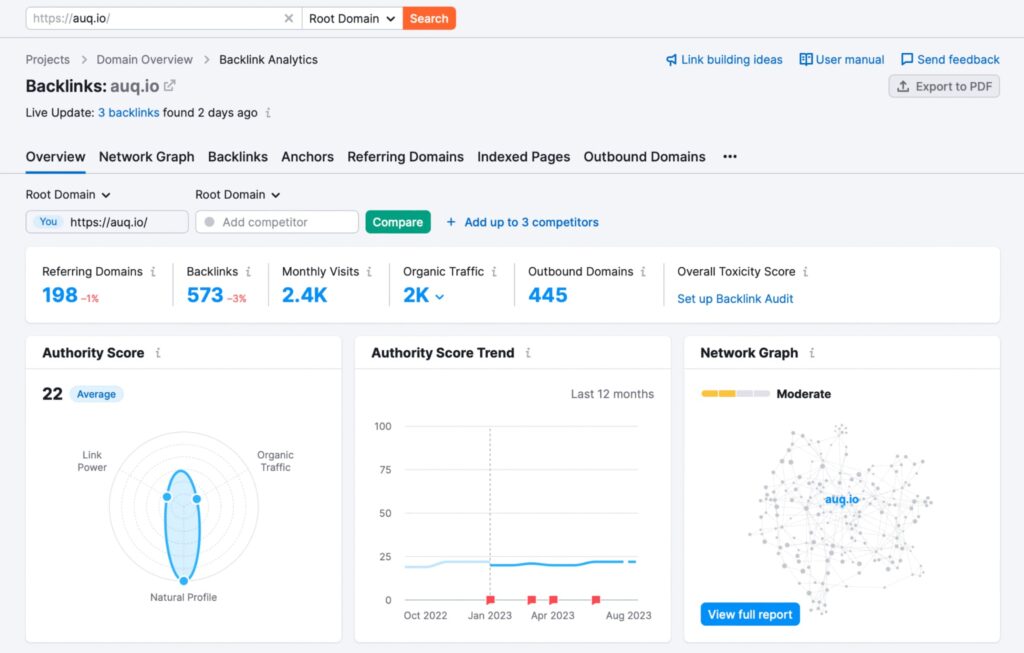
During your migration, reach out to websites linking to your content, and request them to update their links to your new URLs. This process will help maintain your website’s link equity and avoid any negative impacts on your rankings.
8. Track 404 Pages
Closely monitor your website for 404 errors (broken pages) during and after the migration. Use the 404 reports available in webmaster tools like Google Search Console and fix these errors through proper redirects or removed links. Keeping close tabs on this aspect helps maintain your site’s SEO value and user experience.
On-page SEO Best Practices
In addition to your technical SEO considerations during a website migration, it’s essential to implement on-page SEO best practices to maintain your search engine rankings. This section provides an in-depth look at these critical factors.
1. Maintain and Optimize Metadata
One of the things to remember about website migration is that metadata — titles, meta descriptions, alt texts — need to be shifted as they are. Metadata is a direct signal to search engines about your content, and diluting them can have negative effects on your SEO.
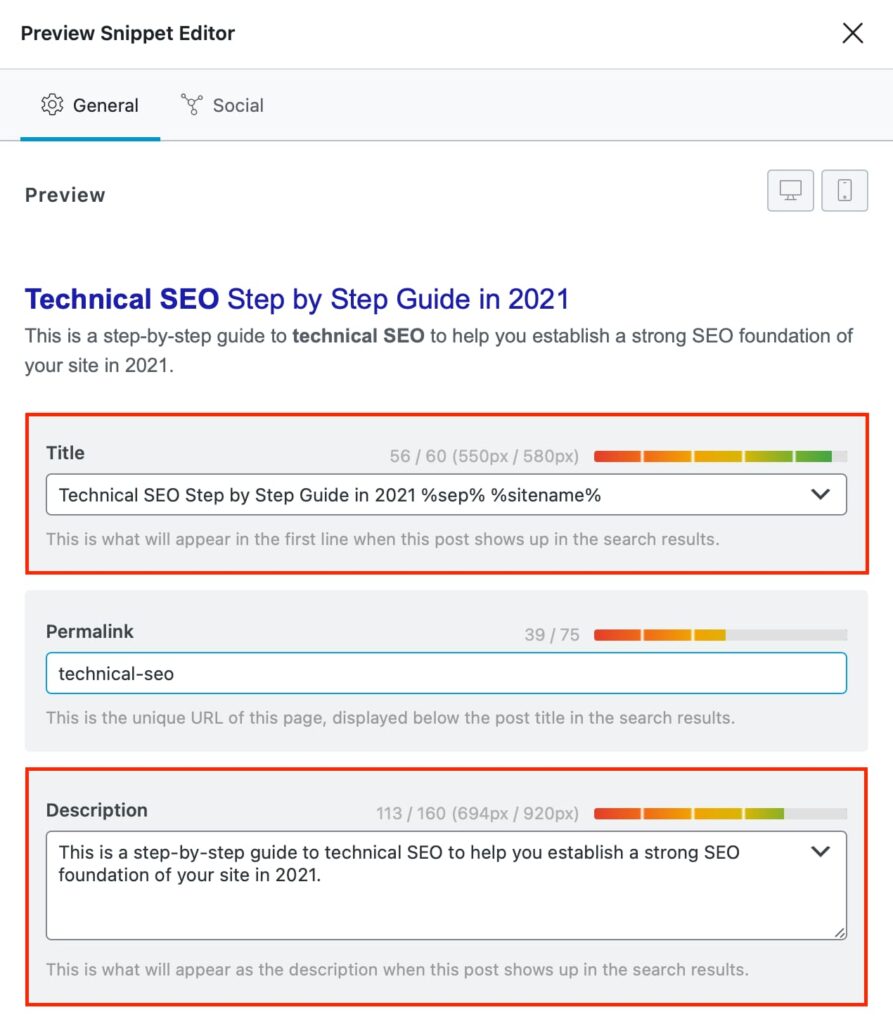
At the same time, migration offers an opportunity to optimize your metadata. You might have overlooked some in the past or have new targeted keywords. Make sure these metadata are concise, descriptive, and within the character limitation set by search engines (typically 60 characters for titles and 155 for descriptions).
2. Content Preservation and Optimization
The quality and relevance of your website’s content play a significant role in search engine rankings. Aim to preserve your existing content during migration while seeking opportunities to optimize and improve.
Utilize keyword research, check the quality of your copy, and ensure that your content aligns with users’ search intent.
Also, examine your content structure, utilizing appropriate headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) for better readability and SEO.
3. Internal Linking Structure
A robust internal linking structure improves user experience and provides clear signals to search engines about your website’s hierarchy and the importance of individual pages.

Examine your website’s interlinking during migration, updating links where necessary to reflect any new URL structures or additional content. Utilize relevant anchor text and avoid over-optimization.
4. Resolve Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content can negatively impact your search engine rankings. Migrating your website offers the perfect opportunity to identify and remedy any duplicate content issues. Utilize tools like Copyscape and Google Search Console to find and remove or revise problematic content.
Ensure that your new website implements the canonical tag correctly to indicate your preferred version of a page and consolidate search engine authority.
5. XML Sitemap and Robots.txt
An XML sitemap is a roadmap for search engines, helping them understand your website’s structure and discover new content. Create an XML sitemap for your new website and submit it to search engines using Google Search Console or other webmaster tools.
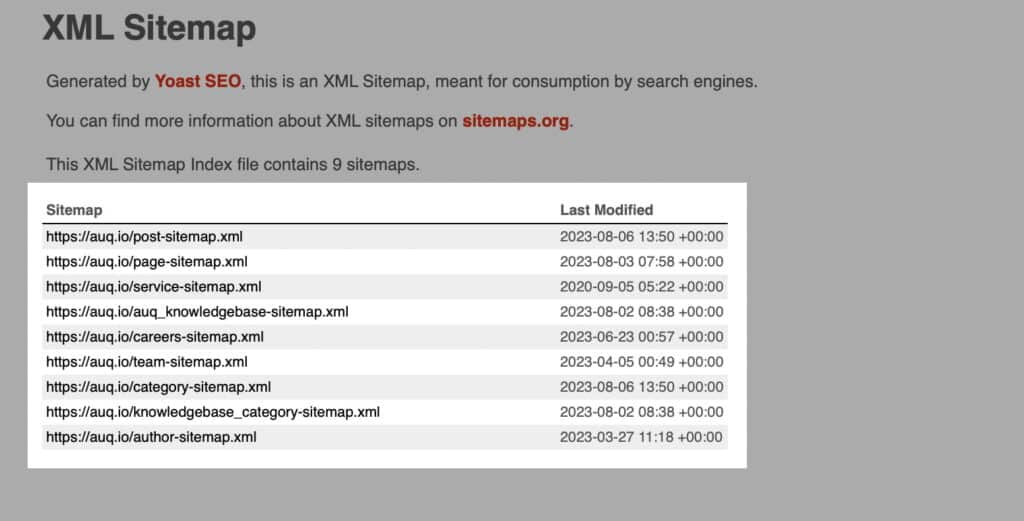
This process will expedite the discovery and indexing of your migrated content. Additionally, update your robots.txt file to manage search engine access and point to the new sitemap location.
6. Keep the Old Domain
While it may seem that getting rid of the old domain after completing the migration process is a good idea, experts advise against it. Your old domain will still have some SEO value for a while, plus, it prevents competitors from taking over that domain.
Reroute any traffic to the old domain to your new site by implementing 301 redirects. This strategy ensures that the user experience stays seamless and that any remaining SEO value from the old domain gets passed to the new website.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
After migrating the site, it’s crucial to keep a close eye on performance to catch any issues before they significantly impact your rankings. There are several things to monitor, and if you’re not well-prepared, this process can easily get overwhelming. So, let’s break this down step by step.
1. Monitor Search Engine Performance
Search engines will start visiting your new site immediately after the move. Regularly checking how they perceive your site is vital to maintain good standings.Primarily, you would want to monitor your organic traffic using Google Analytics. A substantial drop may indicate an issue with the migration, such as missing redirects or inadequately updated sitemaps. If you notice traffic starting to dip, it’s time to dig into the possible causes and fix them.
2. Track Keyword Ranking Changes
During a site migration, your keyword rankings may fluctuate. This is typical and often temporary, as search engines become accustomed to your new site. However, if you notice significant declines, it might indicate a problem.
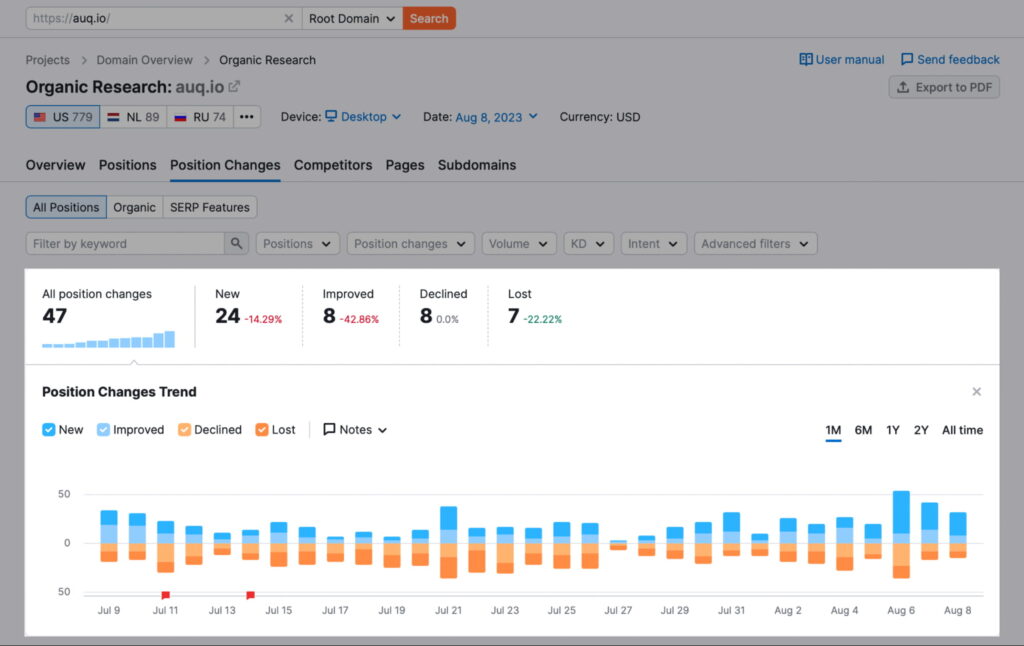
Use your preference of SEO tools to track ranking changes for your targeted keywords. Results below usual standards suggest you need to review your on-page SEO elements, including meta tags, headers, and content quality.
3. Regularly Crawl and Audit the Site
Crawling your site after migration will reveal a lot about what is happening behind the scenes. Crawls can show you unwanted 404 errors, redirects that aren’t working correctly, or perhaps, duplicate content issues.
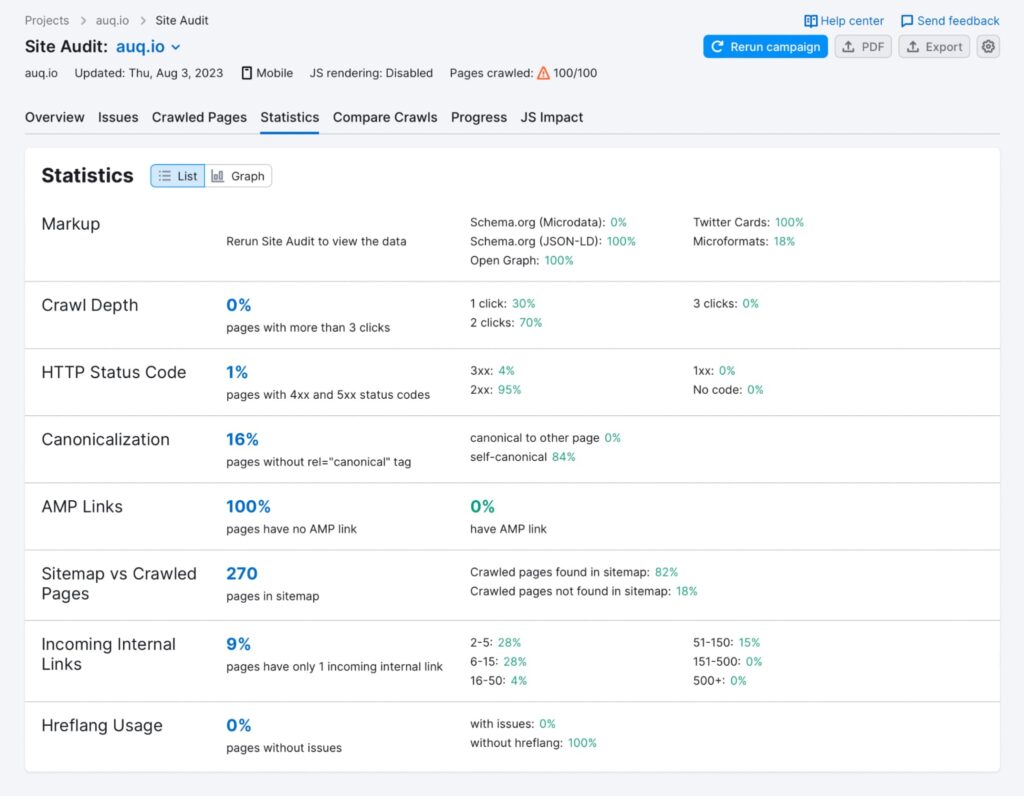
Regular website audits will help identify problems that might be hurting your site’s performance. There are online tools available, like SEMRush and Moz, which can make this one heck of an easier task.
4. Keep an Eye on Google Search Console
Google Search Console will be your best companion throughout the process of monitoring and troubleshooting the SEO elements of your new website. It will alert you on site errors, manual actions, issues regarding structured data, and more.
Moreover, you can monitor your performance on Google search results and keep track of indexing status. An indexation drop in Google Search Console could be a sign of crawling issues, indicating that there might be a problem with your website’s technical aspects.
5. Collect and Utilize User Feedback
Your users can be a source of valuable insights. Feedback from users can help identify issues you might miss, like functionality problems or content inaccuracies.
Also, user behavior data like bounce rate, time spent on site, and page views can be monitored to measure user experience, directly affecting your SEO. Tools like HotJar can be instrumental to collect and analyze user behavior data.
SEO Migration Troubleshooting Tips
Even under the best circumstances, issues can arise during or after website migration. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help rectify any unexpected problems:
- Use Backups Wisely: If a major problem occurs, don’t hesitate to use your backup to restore the site until the issue is resolved.
- Identify Issues Quickly: The sooner you detect and identify the root of an issue, the faster it can be resolved. This principle is why regular auditing and monitoring are so important.
- Leverage Your SEO Toolkit: Tap into the power of SEO tools to investigate issues. Google Search Console is a treasure trove of information for troubleshooting SEO hurdles.
- Ask the SEO Community: If you can’t resolve an issue, don’t be afraid to seek advice from SEO experts or the broader community. Many forums, blogs, and social platforms can provide guidance or direct you to useful resources.
Remember, migration is a structured process – any apparent slip in performance is frequently temporary and recoverable. Ongoing monitoring and readiness to engage with troubleshooting will see you through most migration challenges you stumble upon.
Conclusion
Website migration is more like a tightrope walk; it’s a balancing act between seizing new opportunities for improvement and preserving the SEO value curated over time. Each type of migration, whether it’s linked to platform, domain, protocol, structure, or content, can impact your SEO significantly, highlighting the need for a well-planned and meticulously executed strategy.
Migration can act as a catalyst for business growth or drive down traffic and rankings, depending on how well the process is managed. The key to a successful transition lies in maintaining patience during post-migration fluctuations, regular monitoring for issues, and performing continuous optimization.
In summary, website migration is not just about making substantial changes, it’s also about mitigating the potential SEO risks those changes entail. With the right combination of forethought, precision, and resilience, the migration process can boost your site’s performance and set a sturdy foundation for future growth.