How to Set Up GA4 on a React Website
As the digital realm evolves, so does the need for more sophisticated analytics solutions, and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the avant-garde in this new era. For React developers, setting up GA4 entails more than just plugging in a tracking code; it’s about embracing a data-driven approach that aligns with the dynamic nature of single-page applications (SPAs). From the initial installation of the react-ga4 library to configuring event parameters and triggers, React developers have the tools to track user interactions with unprecedented granularity. Transitioning from React-GA to React-GA4 not only opens doors to richer analytics but also ensures that you remain ahead of the curve in a rapidly shifting analytics landscape.
Integrating GA4 on a React website is a strategic move towards gaining deep insights into how users interact with your application. Build your expertise with a React GA4 tutorial that leads you through setting up tracking for React components, managing the data layer for advanced event tagging, and leveraging the strengths of React-GA4 in a NextJS project. React developers with beginner to intermediate experience in Google Analytics will find that GA4 furnishes a robust set of analytics features, empowering their websites to harness real-time data and user-centric analytics for superior decision-making and enhanced user experience.
| Chapters | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| Initiating GA4 Integration | Embark on your GA4 journey with essential setup guidance for React-based applications, ensuring a seamless analytics property creation and installation. |
| React GA4 Best Practices | Dive into industry best practices for deploying React-GA4, focusing on optimal performance, accuracy in event tracking, and strategic data utilization. |
Initiating GA4 Integration
Kickstarting your integration journey means familiarizing yourself with the lingo of Google Analytics 4 as it pertains to React applications. Grasping these terms is pivotal: they are the building blocks that will empower you to navigate the analytics setup process with clarity and precision. From ‘events’ to ‘properties,’ understanding the vernacular of GA4 will not only streamline the installation but also enhance your ability to extract meaningful insights from your React project’s user data.
- GA4 Property
- An entity within Google Analytics that represents your website or app and is the recipient of the data collected from it.
- React-GA4 Library
- A package that enables React applications to interact with Google Analytics 4, allowing for the tracking of user interactions and the sending of that data to GA4.
- Data Stream
- A flow of user interaction data from your app or website to GA4, designated by a unique stream ID within the GA4 property.
- Tagging
- The process of applying tags to track interactions on your React website, which in turn sends event data to GA4 for analysis.
- Measurement ID
- A unique identifier associated with your GA4 property, necessary for sending event data from your React app.
- Event Name
- The identifier for a type of user interaction that you want to track, such as ‘button_click’ or ‘page_view’.
Transitioning from React-GA to React-GA4
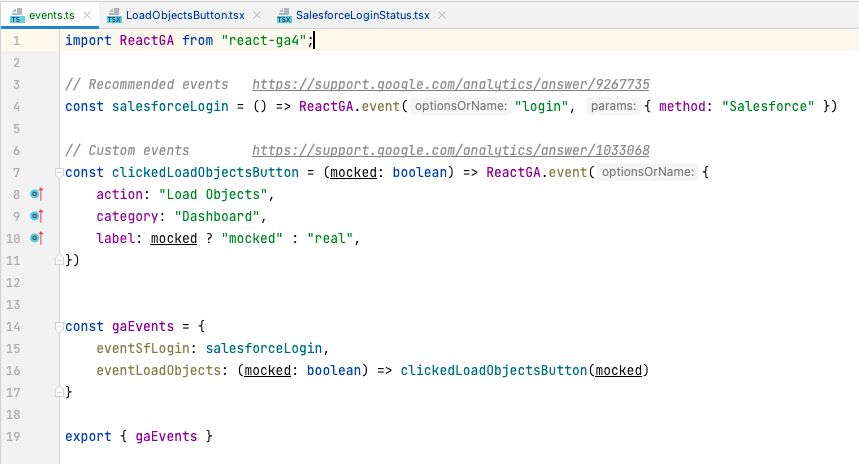
Adapting to React-GA4 from the legacy React-GA library is a critical step for developers looking to harness GA4’s full analytical potential. This transition is not just a mere upgrade; it’s a strategic enhancement to capture more nuanced user data through the new event-based model of GA4.
- Begin by removing React-GA and installing the react-ga4 library.
- Update your codebase to use the ‘gtag’ configuration commands instead of the outdated ‘ga’ commands.
- Revisit your event tracking setup, ensuring it complies with GA4’s schema and leveraging its expanded event and parameter offerings.
This foundational shift sets the stage for advanced tracking capabilities, enabling you to gain deeper insights and a clearer understanding of your users’ behaviors.
React-GA4 Implementation Examples
Concrete examples serve as the best blueprints for learning and implementation, particularly with something as nuanced as tracking in React applications. By examining real-world scenarios, the abstract becomes actionable.
- Analyze a sample React component with GA4 event tracking code, such as tracking button clicks or form submissions.
- Explore a React-GA4 NPM package installation to grasp the ease of integrating analytics into your project.
- Review a case study that demonstrates the integration of React-GA4 in a NextJS project, underscoring the seamless amalgamation of analytics in server-side rendering environments.
These practical demonstrations of React-GA4 harness the library’s capabilities to elevate the analytics infrastructure of any React project to new heights.
React GA4 Best Practices
When it comes to deploying GA4 in your React applications, adhering to best practices can drastically improve the quality of the insights you obtain. In a landscape of event-driven data, the key is in meticulously planning what to track and utilizing the available analytics tools to their utmost potential for a deeper understanding of user engagement.
Ensure that you define clear and meaningful events pertinent to your React app’s user experience. It’s essential to consistently structure event names, parameters, and triggers across the app to maintain data integrity and facilitate analysis. Also, consider user privacy by adhering to data protection regulations like GDPR when configuring your tracking setup.
Remember to test your setup rigorously, and don’t hesitate to leverage the React-GA4’s debugging features to confirm accurate data capture before going live. An effective practice includes the continuous review and update of your analytics strategy to reflect the evolving goals and functionality of your React project.